How to distinguish flat warts from other similar looking skin conditions.
Recently, a client visited the clinic with, what appeared to be, flat warts around the nose, forehead and eyes. However, upon closer inspection an alternative diagnosis was considered. Flat warts can easily be mistaken for other skin conditions. Here we take a look at flat warts and compare them to two similar looking skin condition.
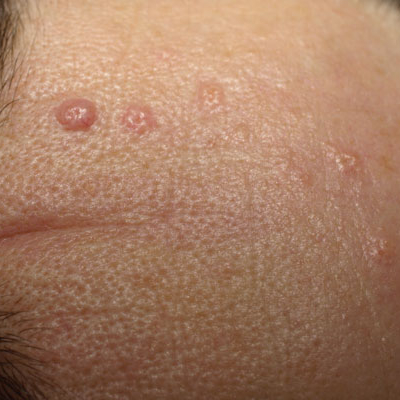
Flat Warts (HPV)
Flat warts are caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV). The virus causes areas of the top layer of skin to thicken. Flat warts are small, between 1-5 mm in diameter, very slightly raised, with a smooth surface and skin coloured. The flat wart virus can be caught by anyone, but is most commonly seen in children, where they usually appear on the face, hands or arms. In women they are usually seen on the legs and in men on the lower half of the face. The flat wart virus can be transferred from close contact with someone who is infected. It can also spread to other areas of the body through cuts and scrapes.
Flat warts can be treated successfully with the Cryopen (cryotherapy), laser or by using home remedies. Warts will usually spontaneously disappear within two years without any treatment.
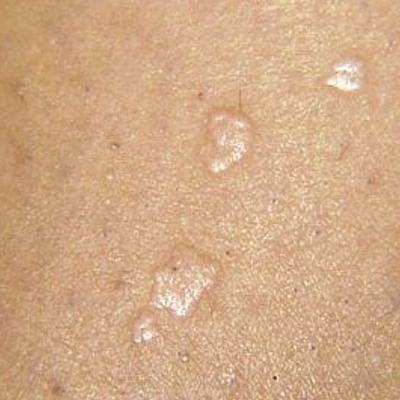
Sebaceous Hyperplasia
Sebaceous Hyperplasia is a condition where the sebaceous glands (oil producing glands) are enlarged. The sebaceous glands are found in the middle to deeper layers of the skin (dermis). They look like small skin coloured bumps, usually with a small depressed area in the centre of the bump, and can be anywhere from 1 mm to several mm in diameter. The surface of the bump can be smooth, slightly uneven or coarse. Sebaceous hyperplasia is benign, not cancerous. The condition is usually seen on the face, especially on the nose, forehead and cheeks, as well as anywhere else on the body where there are many sebaceous glands. Sebaceous Hyperplasia usually appears in middle age or if there is a strong family history of it. It is also more often found in people with fair skin.
Sebaceous hyperplasia can be treated successfully with advanced electrolysis, laser or surgery performed by a dermatologist. The Cryopen is less suitable for removal.
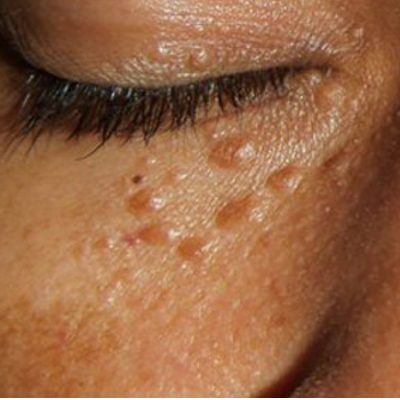
Syringoma
Syringomas are small tumours located in the sweat ducts. Sweat ducts are located in the middle to deeper layers of the skin (dermis). They look like small skin coloured or yellowish firm round bumps, varying in size from 1-3 mm diameter. They are usually found around and under the eyes, but can rarely appear other places on the body. They are benign, not cancerous. Some people are genetically predisposed to getting them. Syringomas are more often found in Asians and people with darker skin.
Syringomas can be treated successfully with laser treatment, advanced electrolysis or excision performed by a dermatologist. The Cryopen is less suitable for removal.